What is a Carbon Credit?
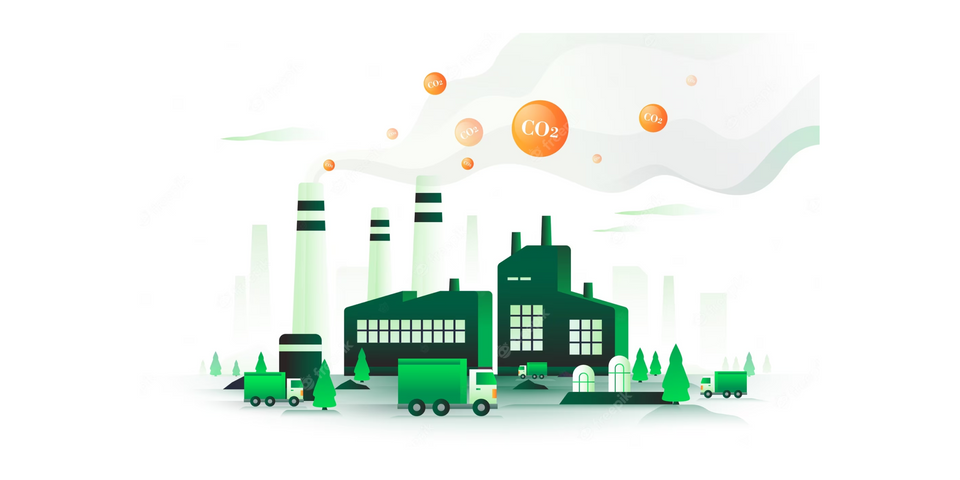

Carbon credits are a key component of carbon trading and carbon offset systems, which aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. A carbon credit represents a unit of measurement that corresponds to the reduction or removal of one metric ton of carbon dioxide (or its equivalent in other greenhouse gases) from the atmosphere.
Carbon credits are typically earned through activities or projects that help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions or enhance carbon sequestration. These activities can include renewable energy projects, reforestation efforts, energy efficiency initiatives, and the implementation of clean technologies.
Once a project or activity is verified to have resulted in emissions reduction or removal, it can generate carbon credits. These credits can then be traded or sold on the carbon market. Buyers of carbon credits, such as individuals, companies, or governments, can use them to offset their own emissions. By purchasing carbon credits, they effectively offset their own carbon footprint and support projects that contribute to global emission reductions.
The concept of carbon credits aims to create financial incentives for emissions reductions and promote sustainable practices. It provides a market-based approach to addressing climate change by encouraging businesses and individuals to take responsibility for their carbon emissions and support initiatives that help mitigate climate change.
FAQ
1. What is a carbon credit?
A carbon credit is a unit of measurement that corresponds to the reduction or removal of one metric ton of carbon dioxide (or its equivalent in other greenhouse gases) from the atmosphere. It is a key component of carbon trading and carbon offset systems aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
2. How are carbon credits earned?
Carbon credits are earned through activities or projects that help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions or enhance carbon sequestration. Examples include renewable energy projects, reforestation efforts, energy efficiency initiatives, and the implementation of clean technologies.
3. What is the purpose of carbon credits?
The purpose of carbon credits is to create financial incentives for emissions reductions and promote sustainable practices. They encourage businesses and individuals to take responsibility for their carbon emissions and support initiatives that help mitigate climate change.
4. How are carbon credits verified?
Projects or activities that generate carbon credits must undergo a verification process to ensure that they have resulted in genuine emissions reduction or removal. This verification is typically conducted by third-party organizations that assess the project's impact and compliance with established standards.
5. How can carbon credits be used?
Carbon credits can be traded or sold on the carbon market. Buyers, such as individuals, companies, or governments, can use them to offset their own emissions. By purchasing carbon credits, they effectively offset their carbon footprint and support projects that contribute to global emission reductions.
6. Who can buy carbon credits?
Individuals, companies, and governments can buy carbon credits. This allows them to offset their carbon emissions and demonstrate their commitment to reducing their environmental impact.
7. What types of projects generate carbon credits?
Projects that generate carbon credits include renewable energy projects (such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power), reforestation and afforestation efforts, energy efficiency projects, methane capture from landfills, and the implementation of clean technologies.
8. What is the role of carbon trading markets?
Carbon trading markets facilitate the buying and selling of carbon credits. They provide a platform where entities that need to offset their emissions can purchase carbon credits from projects that have generated verified emissions reductions.
9. How does the carbon credit system help combat climate change?
The carbon credit system helps combat climate change by providing financial incentives for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. It encourages investment in sustainable projects and technologies, promotes responsible environmental practices, and helps to lower overall global emissions.
10. Are there any regulations governing carbon credits?
Yes, carbon credits are governed by various international, national, and regional regulations and standards. These regulations ensure that the carbon credits are credible, verifiable, and contribute to genuine emissions reductions.
11. Can individuals participate in carbon credit markets?
Yes, individuals can participate in carbon credit markets by purchasing carbon credits to offset their personal carbon footprints. This can be done through various platforms and organizations that offer carbon offset services.
12. What is the difference between carbon credits and carbon offsets?
Carbon credits and carbon offsets are often used interchangeably, but they can have slightly different meanings. Carbon credits refer to the actual units of measurement representing emissions reductions, while carbon offsets refer to the actions taken to compensate for emissions by purchasing carbon credits.




Member discussion